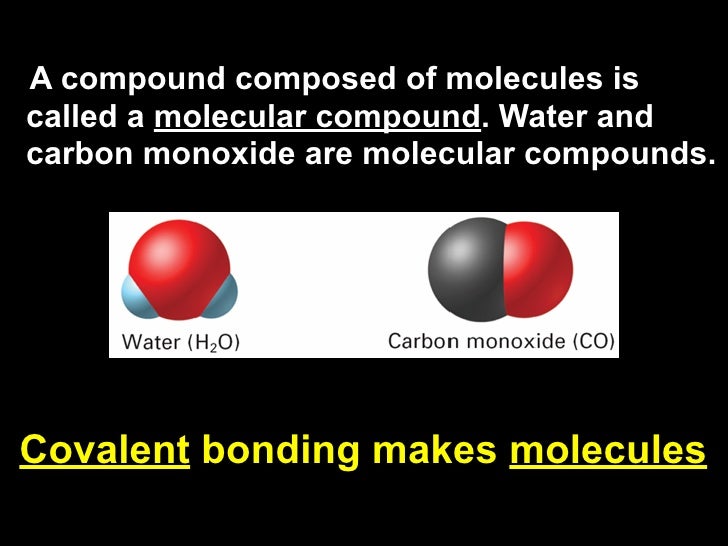
Covalent Compounds Are Composed Of Individual Molecules
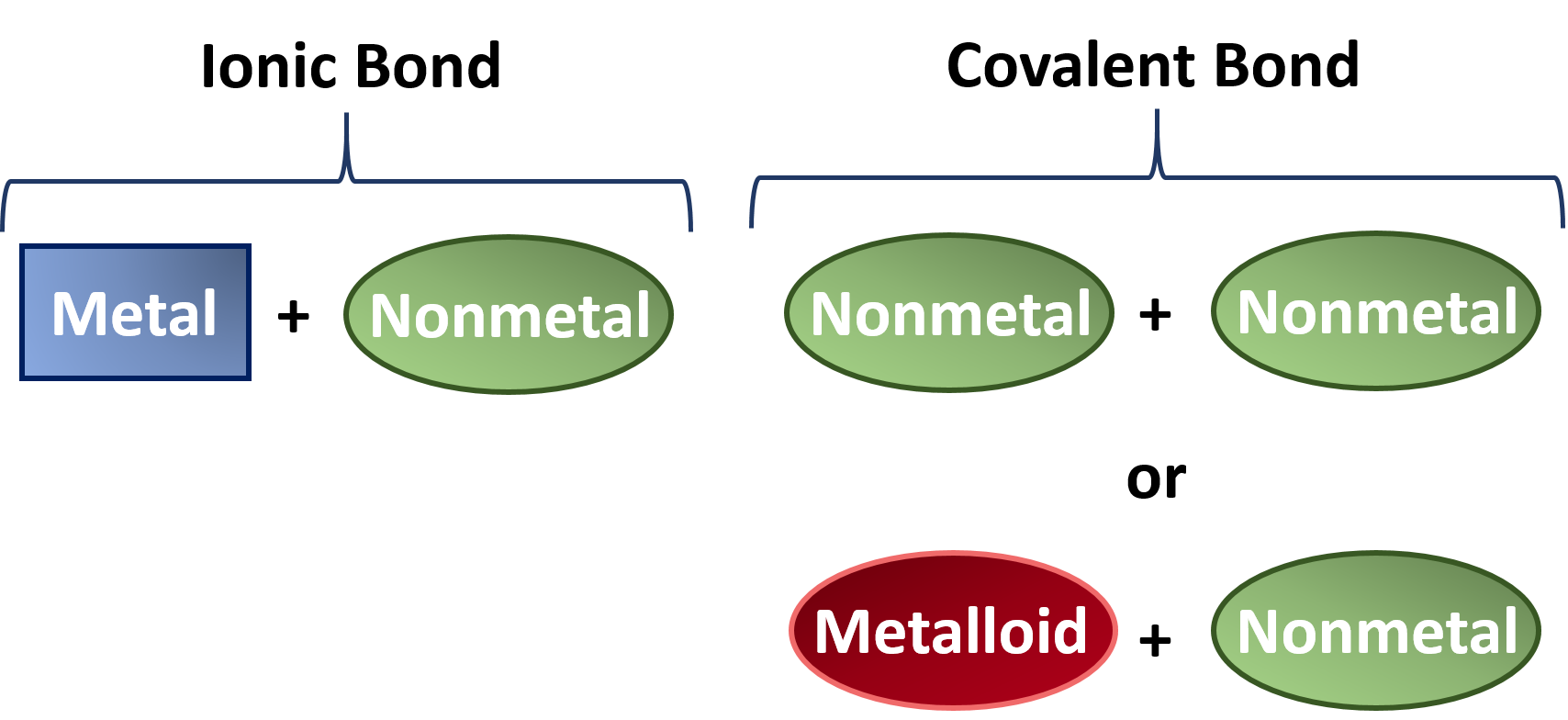
Most covalent molecular structures have low melting and boiling points. Metals often react with nonmetals to form ionic compoundsThese compounds are composed of positive and negative ions formed by adding or subtracting electrons from neutral atoms and molecules.

Section 2 3 Covalent Compounds Covalent Compounds In This Section A The Nature Of Covalent Compounds B Ways Of Representing Covalent Compounds C Naming Ppt Download
The enthalpy of fusion is the amount of energy that is required to melt a solid.

Covalent compounds are composed of individual molecules. In the kinetic theory of gases the term molecule is often used. Not all chemical bonds are created equal. The molecules that make up living things are covalently bonded for example and covalent bonds are more common in nature than ionic bonds overall.
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. Due to the difference in bonding styles covalent bonds can form between atoms of the same element such as hydrogen gas which has the formula H 2 but ionic bonds cant. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their lack of electrical charge.
Any large molecule is referred to as macromolecule macro- large and the organic compounds in this section all fit this description. A different attractive interaction between atoms called covalent bonding is involved here. Carbons affinity for covalent bonding means that many distinct and relatively stable organic molecules nevertheless readily form larger more complex molecules.
None of these compounds is composed of ions. Elements combine to form chemical compounds that are often divided into two categories. In chemistry polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end.
Molecules containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond. In quantum physics organic chemistry and biochemistry the distinction from ions is dropped and molecule is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. The world is generally not composed of isolated atoms.
However it is important to note that the bond formed between two individual water molecules is a hydrogen bond and not covalent. The polar covalent character of water allows its molecules to become attracted to many other different types of molecules and disrupt their pre-existing bonds. Water is a liquid at room temperature.
Carbon dioxide and carbon tetrafluoride are gases. Rather atoms bond to one another to form molecules and hence chemical compounds. This is because the intermolecular forces between covalent molecules require a lower amount of energy to separate from each other.
Some are weak and some very strong a difference that depends primarily on. Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Covalent molecular compounds usually have a low enthalpy of fusion and vaporization due to the same reason.
The other three reactions shown above give products that are very different from sodium chloride.
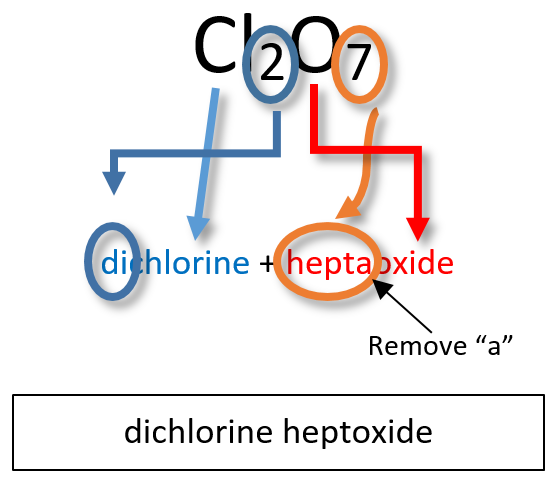
Ch150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds And Molecular Compounds Chemistry
Ch150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds And Molecular Compounds Chemistry

Atomic Structure Classwork Homework By Threefourthsme Tpt Atomic Structure Word Problems Atomic Theory

Molecular And Ionic Compounds Chemistry For Majors
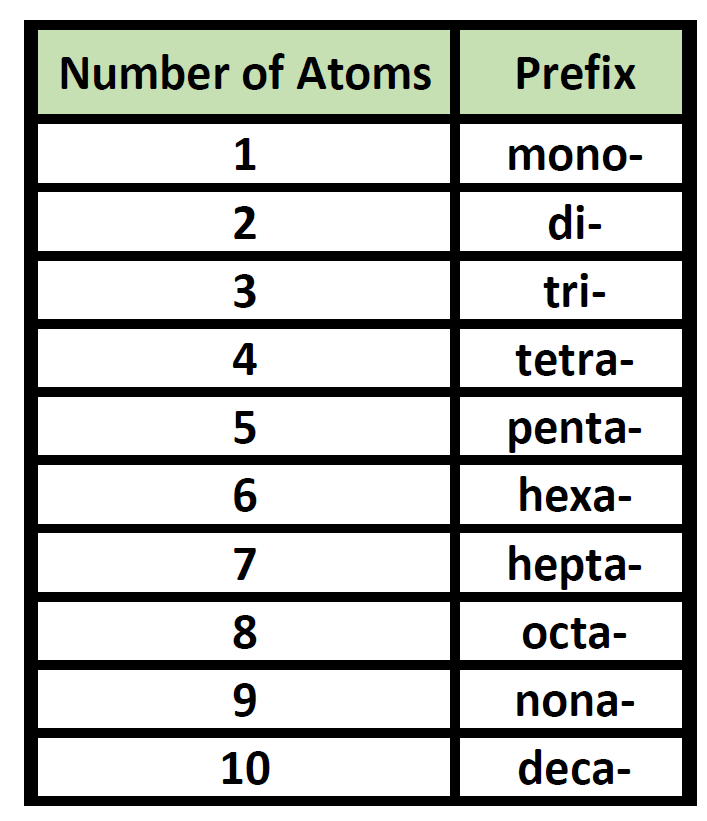
Ch150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds And Molecular Compounds Chemistry
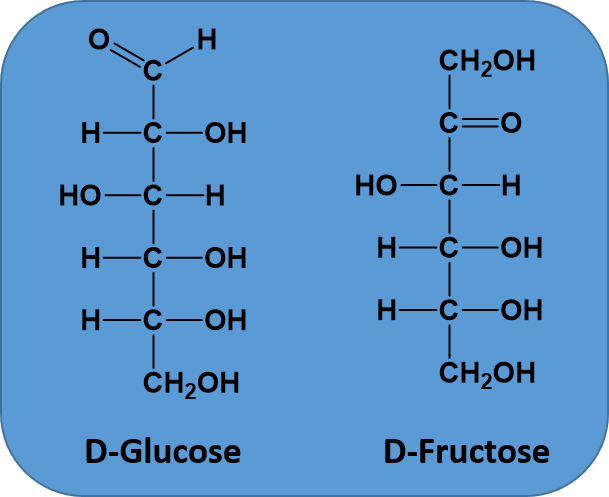
Ch103 Chapter 5 Covalent Bonds And Introduction To Organic Molecules Chemistry
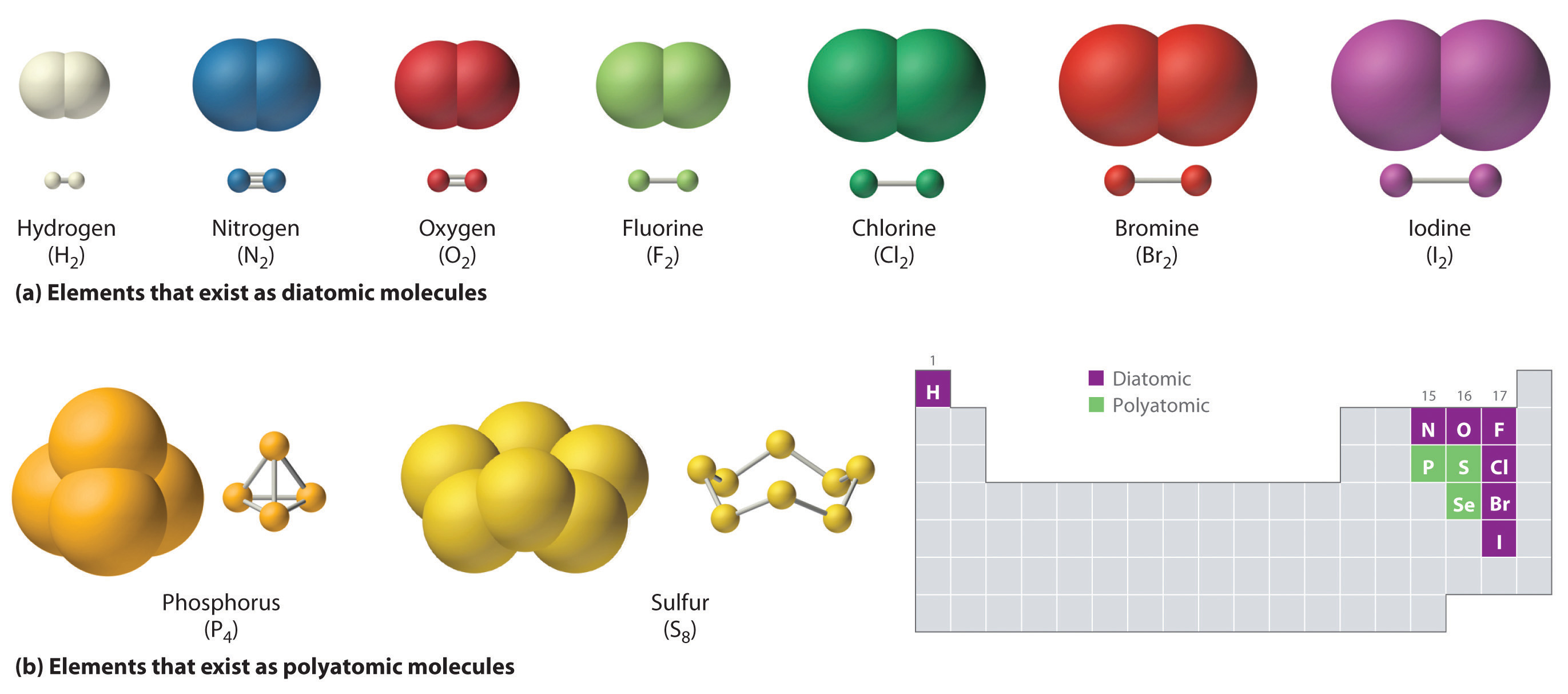
Ch150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds And Molecular Compounds Chemistry

Bond Order Discrimination By Atomic Force Microscopy Chemical Bond Science Microscopy

Section 2 3 Covalent Compounds Covalent Compounds In This Section A The Nature Of Covalent Compounds B Ways Of Representing Covalent Compounds C Naming Ppt Download

Dna Structure Cornell Doodle Notes Distance Learning Doodle Notes Science Notes Science Teaching Resources

Elements Atoms Molecules Ions Ionic And Molecular Compounds Cations Vs Anions Chemistry Youtube Compounds Science Chemistry Classroom Chemistry Lessons

Section 8 1 Are Electrons Only Transferred While Studying Ionic And Metallic Bonding Electrons Have Been Mov Covalent Bonding Ionic Bonding Metallic Bonding
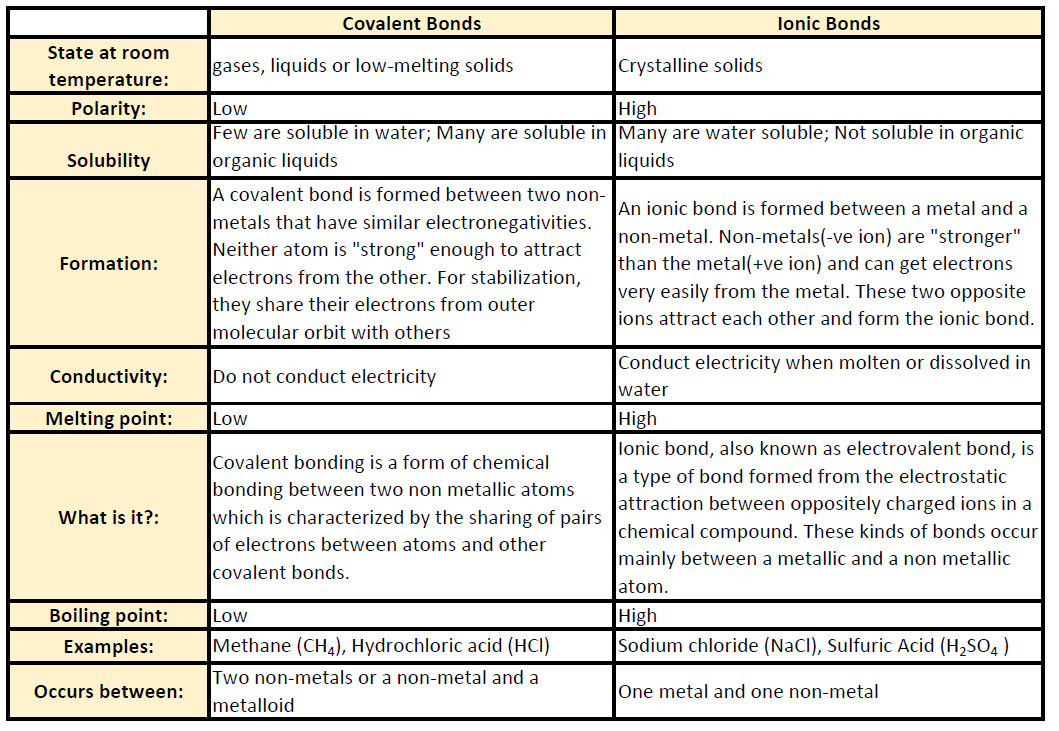
Ch150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds And Molecular Compounds Chemistry

Regular Bio Life S Levels Of Organization Teaching Biology Daily Vocabulary Words Organization

Ch150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds And Molecular Compounds Chemistry
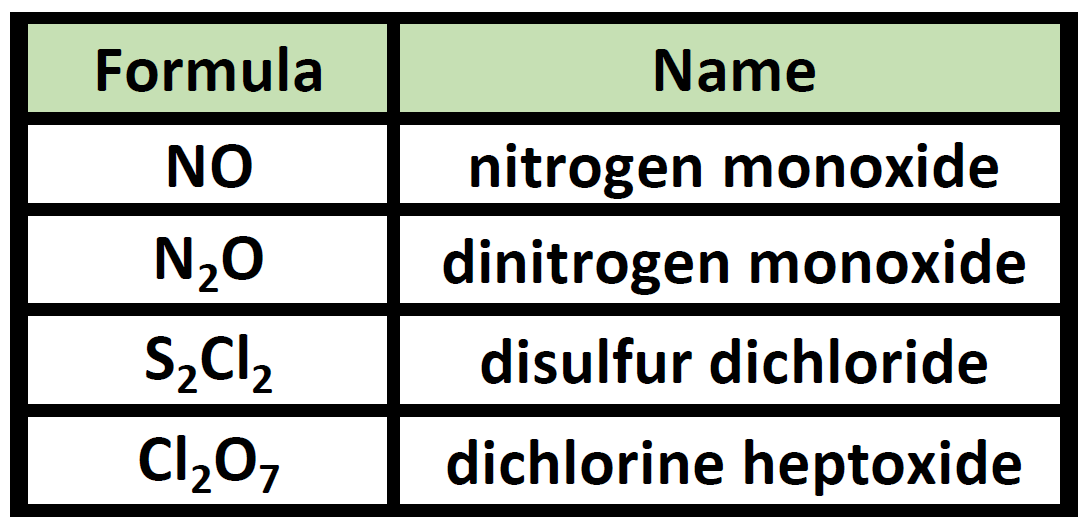
Ch150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds And Molecular Compounds Chemistry

Ionic And Covalent Compounds Ppt Download

Covalent Bond Definition Properties Examples Facts Britannica